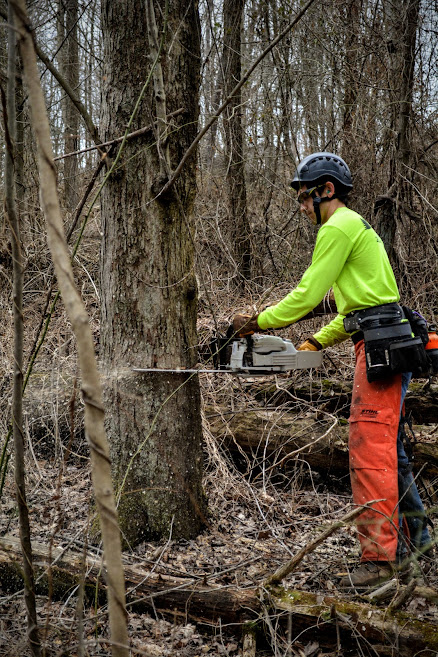
The Benefits of Forest Thinning
Healthy forests provide many benefits such as watershed protection, aesthetic beauty, timber value, recreational opportunities, and wildlife habitat. Through proper forest management and improvement techniques, such as thinning, we are able to sustain, improve, and protect forest health, while increasing timber value and improving wildlife habitat.
What is Forest Thinning?
Thinning is a timber stand improvement (TSI) technique performed in stands with higher than optimum stocking levels. Trees are selected for removal to favor the growth, health, and development of the remaining trees, by reducing the effects of competition and allowing the standing trees to grow more efficiently. Overstocked stands are characterized by high mortality rates, lack of understory development, slow timber growth, and reductions in the living crowns of trees. By opening up the canopy and freeing space in the understory, it allows for more access to sunlight, water, and nutrients, thereby increasing productivity of the selected crop trees and promoting regenerating in the understory, thus increasing the overall the growth productivity of the stand. There are a variety of forest thinning practices, such as but not limited to, crop tree release, row thinning, and mid-story removal. The recommended thinning practice varies by the overall management objective and the current composition/condition of the timber stand.

Benefits of Thinning: Positive Effects on Timber Value
Forest thinning operations can be used to increase timber value of a stand by:
- Increasing growth rates by reducing the time it takes for trees to reach maturity.
- Altering the species composition of a stand with the aim of increasing the proportion of valuable timber species.
- Increasing the proportion of valuable wood volume by decreasing the amount of poor-formed, low-quality, and over-mature trees.
According to two Purdue Extension foresters, annual rates of return from a forest improvement operation, such as thinning, often average 10 to 15%! An example of rate of return from TSI on an average woodlot is provided in Appendix A of Purdue Extension’s Forest Improvement Handbook.
Benefits of Thinning: Positive Effects on Wildlife Habitat
Forest thinning operations can be used to improve wildlife habitat by:
- Altering the species composition of a stand with the aim of increasing the proportion of tree species providing valuable sources of food and shelter, such as oak and hickory species.
- Altering the age class of forest. Even-aged stands, those consisting of a distinct age and size class, are less diverse and benefit fewer species of wildlife in comparison to balanced, uneven-aged stands consisting of three or more age and size classes.
- Removing invasive trees, shrubs, and vines which are detrimental to the overall health and quality of a habitat.
For more information on how thinning is an important tool used in wildlife management, read this article produced by the Arkansas Game and Fish Commission.
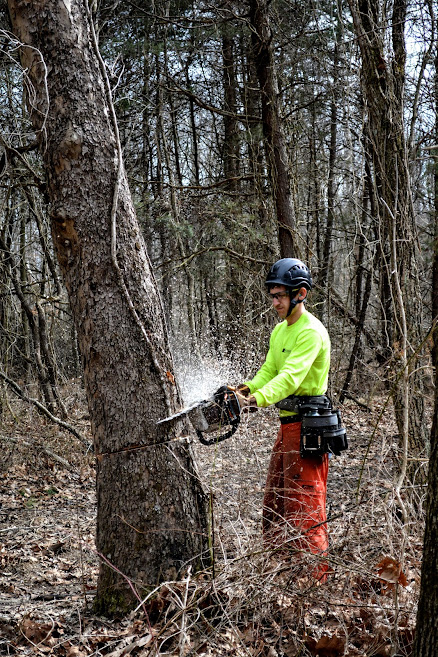

Conclusion
Thinning operations are investments into the future of a forestland to be used to increase timber value and/or improve wildlife habitat quality, and may be incorporated into a written forest and wildlife habitat management plan. Such management plans can be used to apply for federal and state cost-share programs to help pay for the cost of forest thinning and other forest improvement operations. Contact us, your district forester, or your district conservationist, for more information on enrolling in cost-share programs.
Contact us to discuss whether forest thinning is recommended on your property and how we can help you reach your timber management and/or wildlife habitat management goals.